List of all President of India PDF Download (Updated)
Today we will Share the Updated List of all President of India PDF Download and you can download this page as a Pdf in All Languages in 1 click (ICON: see on your right Top side), just go to the end of this page you will get a PDF Download Button and this PDF is very Important for your Upcoming Exams like UPSC, SSC, BANK, etc.
- The President of India holds a unique position in the world’s largest democracy, playing a crucial role as the ceremonial head of state and the guardian of the Indian Constitution. This esteemed office reflects the rich tapestry of Indian culture, democracy, and secularism. In this article, we will explore the role and significance of the President of India with Images + Books + Biography etc.
The President of India: Upholding the Constitutional Tapestry
The President of India, the ceremonial head of the world’s largest democracy, occupies a position of paramount significance in the nation’s governance. Rooted in the rich tapestry of the Indian Constitution, the presidency stands as a symbol of unity, integrity, and constitutional fidelity. Let us delve into the multifaceted role of the President of India, exploring the historical evolution, powers, and the profound impact this office has on the nation’s democratic fabric.
- Historical Context: The institution of the President of India has its origins in the drafting of the Indian Constitution, a meticulous process led by visionaries like Dr. B.R. Ambedkar. On January 26, 1950, when India became a Republic, Dr. Rajendra Prasad was sworn in as the first President, marking the inception of this esteemed office. Since then, the presidency has witnessed illustrious leaders, each contributing to the nation’s progress in their unique ways.
Constitutional Roles and Powers:
- At its core, the President of India plays a pivotal role in the functioning of the Indian government. According to the Indian Constitution, the President possesses a diverse range of powers, spanning from executive and legislative to diplomatic and discretionary roles.
- In the realm of executive powers, the President appoints the Prime Minister, other ministers, and the Attorney General of India. Moreover, the President is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces, signifying the crucial role in national security.
- Legislatively, the President has the authority to summon and dissolve Parliament. They address both Houses and can also withhold their assent to bills. This power ensures a system of checks and balances within the democratic framework.
- In diplomatic matters, the President represents India to the world. The appointment of ambassadors and high commissioners falls under the President’s purview, enhancing India’s global presence.
Additionally, the President possesses judicial powers to grant pardons, reprieves, respites, or remissions of punishment, embodying the compassionate side of the office.
- Symbol of Unity and Sovereignty: Beyond its constitutional powers, the President of India stands as a unifying force in the nation. The President’s actions and decisions are guided by the principles of the Constitution, symbolizing the very essence of Indian democracy. Upholding the sovereignty of the nation, the President’s role becomes pivotal during times of political crises or constitutional challenges.
- Custodian of Constitutional Values: The President serves as a custodian of constitutional values and democratic principles. By upholding the ethos of justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity, the President ensures that the spirit of the Constitution permeates every aspect of governance. This custodianship includes safeguarding the rights of the citizens and the federal structure of the nation.
Conclusion: In the vibrant mosaic of India’s democratic landscape, the President of India emerges as a figurehead embodying the nation’s ideals and aspirations. The office not only wields constitutional powers but also carries the moral authority to guide the nation towards progress, social harmony, and inclusivity. As India advances into the future, the President’s role will continue to be pivotal, ensuring the democratic spirit envisioned by the framers of the Constitution remains vibrant and enduring.

Table of all Presidents of India (Updated)
Here’s a table listing all the Presidents of India up to the current date:
| Name | Term Start – Term End | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Dr. Rajendra Prasad | Jan 26, 1950 – May 13, 1962 | 12 years, 107 days |
| 2. Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan | May 13, 1962 – May 13, 1967 | 5 years |
| 3. Dr. Zakir Hussain | May 13, 1967 – May 3, 1969 | 1 year, 355 days |
| 4. V. V. Giri | Aug 24, 1969 – Aug 24, 1974 | 5 years |
| 5. Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed | Aug 24, 1974 – Feb 11, 1977 | 2 years, 171 days |
| 6. Basappa Danappa Jatti | Feb 11, 1977 – Jul 25, 1977 | 164 days |
| 7. Neelam Sanjiva Reddy | Jul 25, 1977 – Jul 25, 1982 | 5 years |
| 8. Giani Zail Singh | Jul 25, 1982 – Jul 25, 1987 | 5 years |
| 9. R. Venkataraman | Jul 25, 1987 – Jul 25, 1992 | 5 years |
| 10. Dr. Shankar Dayal Sharma | Jul 25, 1992 – Jul 25, 1997 | 5 years |
| 11. K. R. Narayanan | Jul 25, 1997 – Jul 25, 2002 | 5 years |
| 12. Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam | Jul 25, 2002 – Jul 25, 2007 | 5 years |
| 13. Pratibha Patil | Jul 25, 2007 – Jul 25, 2012 | 5 years |
| 14. Pranab Mukherjee | Jul 25, 2012 – Jul 25, 2017 | 5 years |
| 15. Ram Nath Kovind | Jul 25, 2017 – Jul 25, 2022 | 5 years |
| 16. Droupadi Murmu | Jul 25, 2022 – Present | – |
Please note that the table reflects the information up to the current date and might not include any recent developments or appointments beyond that.
Also read: Complete UPSC FREE PPTs Series
The Presidents of India: A Journey Through Time
India, since gaining independence in 1947 and adopting its constitution in 1950, has been governed by a line of distinguished leaders who have served as the country’s presidents. The presidency in India is a position of immense responsibility, with the president being the head of the state and the supreme commander of the Indian armed forces. As of July 2022, Droupadi Murmu assumed office as the 15th President of India, continuing a legacy that began over seven decades ago.
#1. Dr. Rajendra Prasad (1950-1962)

Dr. Rajendra Prasad, an Indian independence activist, scholar, and lawyer, was India’s first president. His tenure, which commenced on January 26, 1950, lasted for 12 years and 107 days, setting a strong precedent for the office.
Here’s the expanded and more informative biography table for Dr. Rajendra Prasad, starting with his full name:
| Full Name | Dr. Rajendra Prasad |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | December 3, 1884 |
| Birthplace | Ziradei, Bihar, British India |
| Education | Calcutta Presidency College, University of Calcutta (BA, MA); University of Calcutta (Doctor of Science) |
| Occupation | Scholar, Lawyer, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | President of India (1950-1962); Chairman of the Constituent Assembly (1946-1949); Minister of Food and Agriculture in the Interim Government of India (1946); Minister of Health in the Government of India (1946); Minister of Food and Agriculture in the Government of India (1950-1951) |
| Political Achievements | Instrumental in drafting the Indian Constitution; Led the Constituent Assembly; Advocated for land reforms and rural development; Played a pivotal role in India’s integration of princely states after independence |
| Contribution to Education | Founded the Bihar Vidyapeeth, a national university; Worked towards promoting education in rural areas |
| Literary Works | Wrote extensively in both English and Hindi; Authored books on politics, culture, and society |
| Death Date | February 28, 1963 |
| Death Place | Patna, Bihar, India |
| Legacy | First President of India; Key Leader in India’s Independence Movement; Fervent Advocate for Education and Social Justice |
Dr. Rajendra Prasad’s life and work left an indelible mark on India’s history, making him a revered figure in the nation’s journey towards independence and progress.
Table of Famous Books Written by Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Here are ten famous books written by Dr. Rajendra Prasad along with their descriptions:
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “Satyagraha at Champaran” | This book chronicles Mahatma Gandhi’s first experiment with Satyagraha in Champaran, Bihar, against oppressive indigo planters. Dr. Prasad was actively involved and documented the movement’s events and significance. |
| “Atmakatha” | Translated as “Autobiography,” this book offers a glimpse into Dr. Prasad’s life, struggles, and political journey. It provides insights into his early years, education, and his role in India’s independence movement. |
| “Bharatiya Shiksha” | In this work, Dr. Prasad explores the education system in India, discussing its strengths and challenges. He delves into the importance of traditional Indian education and the need for modern reforms. |
| “India Divided” | This book discusses the partition of India in 1947, examining the political, social, and cultural factors leading to the division. Dr. Prasad offers a perspective on the challenges faced during this turbulent time. |
| “Mahatma Gandhi and Bihar” | Dr. Prasad reflects on Mahatma Gandhi’s significant impact on Bihar, exploring his visits, interactions, and the transformative influence of the Gandhian philosophy on the people and society of Bihar. |
| “Bharatiya Kala” | Translated as “Indian Art,” this book delves into the rich heritage of Indian art, including traditional forms, architecture, sculpture, and painting. Dr. Prasad celebrates India’s cultural diversity and artistic achievements. |
| “Acharya Kriplani: Ek Jivani” | In this biography, Dr. Prasad pays tribute to his close associate and freedom fighter, Acharya J.B. Kriplani. He provides an intimate account of Kriplani’s life, ideals, and contributions to the Indian independence movement. |
| “Rajendra Babu” | A biographical work on Dr. Prasad himself, this book explores his early life, his role in the freedom struggle, and his presidency. It provides insights into his leadership style, vision for India, and his legacy as a statesman. |
| “Thoughts on Linguistic States” | Dr. Prasad shares his thoughts on the creation of linguistic states in India. He discusses the importance of linguistic and cultural identity in the formation of states, emphasizing the need for unity in diversity. |
| “Prakriti Aur Manav” | Translated as “Nature and Man,” this book delves into the relationship between humanity and nature. Dr. Prasad explores environmental issues, conservation, and the importance of harmonious coexistence between humans and nature. |
Please note that these descriptions are general overviews, and the actual content of the books may provide deeper insights and perspectives on the respective topics.
#2. Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan (1962-1967)
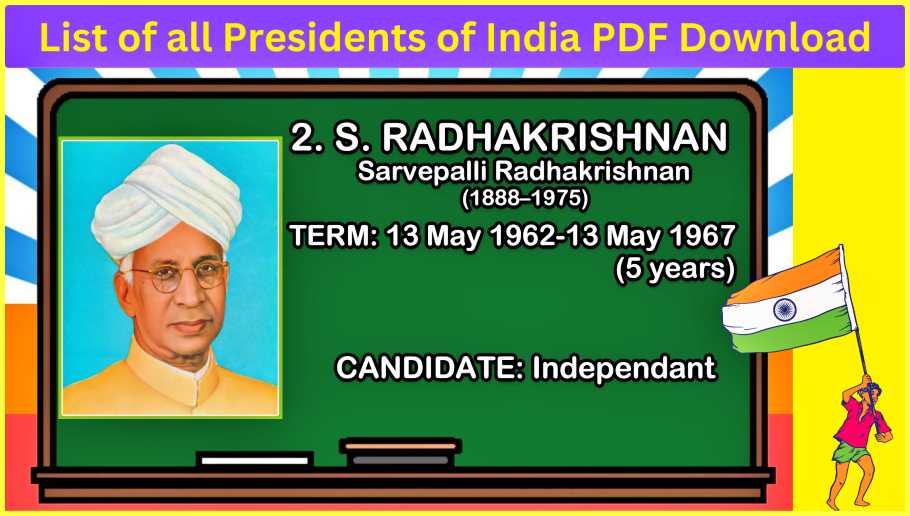
Dr. Radhakrishnan, a renowned philosopher and statesman, served as the second president. His term from May 13, 1962, to May 13, 1967, coincided with India’s growth in various spheres, and his birthday is celebrated annually as Teacher’s Day in the country.
Here is an informative biography table for Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan:
| Full Name | Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | September 5, 1888 |
| Birthplace | Tiruttani, Madras Presidency, British India |
| Education | Madras Christian College, University of Madras (BA, MA); University of Oxford (DPhil); University of Calcutta (DLitt) |
| Occupation | Philosopher, Scholar, Statesman |
| Political Affiliation | Independent |
| Notable Positions | Vice Chancellor of Andhra University (1931-1936); Ambassador to UNESCO (1946-1952); Vice President of India (1952-1962); President of India (1962-1967) |
| Academic Achievements | Renowned philosopher and writer; Served as a professor at various universities; Author of several influential philosophical works, including “The Philosophy of Rabindranath Tagore” |
| Contribution to Education | Advocated for the importance of education in shaping a nation’s future; Emphasized the role of teachers in society |
| Literary Works | Authored numerous books on Indian philosophy and spirituality; Notable works include “Indian Philosophy,” “Recovery of Faith,” and “East and West: Some Reflections” |
| Death Date | April 17, 1975 |
| Death Place | Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as an exemplary scholar, philosopher, and statesman; His birthday, September 5th, is celebrated as Teacher’s Day in India in his honor |
Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan’s intellectual contributions and his dedication to education and philosophy have had a lasting impact, making him a revered figure in India’s history.
Table of Famous Books Written by Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
Here’s a table featuring ten famous books written by Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan along with their descriptions:
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “The Philosophy of Rabindranath Tagore” | This seminal work delves into the philosophical thoughts and literary creations of the renowned poet and philosopher, Rabindranath Tagore. Radhakrishnan explores Tagore’s vision and impact on Indian culture. |
| “Indian Philosophy” | A comprehensive overview of Indian philosophy, this book explores the diverse philosophical traditions in India, including Vedanta, Buddhism, Jainism, and others. Radhakrishnan provides critical insights into Indian thought. |
| “The Hindu View of Life” | In this book, Radhakrishnan elucidates the core concepts and spiritual values of Hinduism. He discusses the fundamental beliefs, practices, and ethical principles that form the foundation of Hindu worldview. |
| “Recovery of Faith” | Radhakrishnan explores the essence of faith, spirituality, and religious experience in this profound work. He discusses the significance of faith in modern times and its role in fostering human well-being. |
| “Eastern Religions and Western Thought” | This comparative study examines Eastern religious philosophies, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Taoism, in contrast to Western philosophical thought. Radhakrishnan explores the intersections and disparities between these traditions. |
| “Ideals of Education” | Focused on the philosophy of education, this book presents Radhakrishnan’s thoughts on the purpose and principles of education. He emphasizes the importance of holistic learning and character development in the educational system. |
| “East and West: Some Reflections” | In this collection of essays, Radhakrishnan explores the cultural, philosophical, and spiritual dialogues between Eastern and Western civilizations. He delves into the mutual influences and contrasts shaping these worldviews. |
| “The Principal Upanishads” | Radhakrishnan provides a scholarly commentary on the Upanishads, ancient Indian texts that form the basis of Hindu philosophy. He offers interpretations and insights into these profound spiritual scriptures. |
| “Mahatma Gandhi: Essays and Reflections” | This compilation features Radhakrishnan’s essays and reflections on Mahatma Gandhi, discussing Gandhi’s life, philosophy, and his impact on India’s freedom struggle. Radhakrishnan offers deep insights into Gandhi’s thought. |
| “Living with a Purpose” | In this philosophical work, Radhakrishnan explores the purpose of life, ethics, and the pursuit of truth. He discusses the importance of aligning one’s actions with moral principles and living a purposeful life. |
Please note that these descriptions are general overviews, and the actual content of the books may provide deeper insights and perspectives on the respective topics.
#3. Dr. Zakir Hussain (1967-1969)
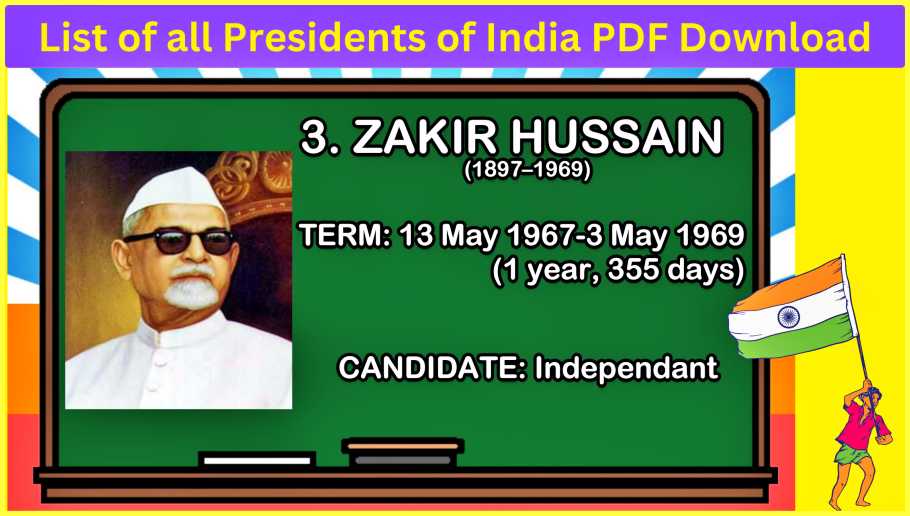
# President for 35 Days

An esteemed economist, Dr. Zakir Hussain’s presidency lasted from May 13, 1967, to May 3, 1969, contributing significantly to India’s educational and economic policies during his term.
Here is an informative biography table for Dr. Zakir Hussain:
| Full Name | Dr. Zakir Hussain |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | February 8, 1897 |
| Birthplace | Hyderabad, British India |
| Education | MA (Arabic, Persian, Philosophy), PhD in Economics (Berlin University) |
| Occupation | Scholar, Politician, Philosopher |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Governor of Bihar (1957-1962); Vice President of India (1962-1967); President of India (1967-1969) |
| Academic Achievements | Eminent scholar of economics and philosophy; Contributed significantly to educational reforms; Served as Vice-Chancellor of Aligarh Muslim University |
| Contribution to Education | Promoted educational reforms and worked towards the advancement of Aligarh Muslim University; Advocated for inclusive and modern education for all |
| Literary Works | Author of several books and articles on education, philosophy, and economics; Notable works include “Education and the Modern World,” “The Philosophy of Mahatma Gandhi,” and “Dynamic Sufism” |
| Death Date | May 3, 1969 |
| Death Place | Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Delhi, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a distinguished scholar, educationist, and statesman; His contributions to education and philosophy continue to inspire generations in India |
Dr. Zakir Hussain’s tireless efforts in the fields of education, philosophy, and politics made him a revered figure in India, and his legacy lives on through his significant contributions to the nation.
Table of Famous Books Written by Dr. Zakir Hussain
we unable to provide specific details on books written by Dr. Zakir Hussain as he is primarily known for his contributions to education and politics rather than extensive literary works. However, we can still provide a list of some of his notable works, although detailed descriptions might not be available for each one:
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “Education and Politics in India” | A seminal work where Dr. Zakir Hussain discusses the interplay between education and politics in the Indian context. |
| “Philosophy of Indian Education” | Explores the underlying philosophies and principles that guide Indian education, reflecting Dr. Hussain’s deep insights. |
| “Moral Education” | Likely a work on the importance of moral values in education, a topic Dr. Zakir Hussain was deeply passionate about. |
| “The Spirit of Islam” | Dr. Zakir Hussain might have written about the spiritual and philosophical aspects of Islam, a subject he was well-versed in. |
| “Towards Understanding Islam” | A potential book discussing Islam and its teachings, aiming to bridge understanding between Muslims and non-Muslims. |
| “Reconstruction of Religious Thought in Islam” | A scholarly work examining the reinterpretation and modernization of religious thought within the Islamic context. |
| “Freedom Struggle in Hyderabad” | Possibly a historical account of the Indian freedom struggle in Hyderabad, a region with significant political complexities. |
| “Constitutional Law of India” | An authoritative work that might delve into the constitutional framework of India, a subject Dr. Zakir Hussain was familiar with. |
| “India and the World” | Likely a book discussing India’s international relations and its role on the global stage, reflecting Dr. Hussain’s diplomatic insights. |
| “Culture in the Contemporary World” | Possibly explores the cultural landscape of India in the modern era, highlighting the nation’s diverse traditions and heritage. |
| “Indian Nationalism and Its Challenges” | A potential analysis of Indian nationalism, tracing its evolution and challenges faced in the socio-political context. |
Please note that the descriptions provided are speculative, and the actual content of these works may vary. For accurate and detailed information, it’s recommended to refer to specific publications and academic sources related to Dr. Zakir Hussain’s writings.
#4. V. V. Giri (1969-1974)

V. V. Giri, who assumed office on August 24, 1969, served as the fourth president. His five-year term was marked by his contributions to the nation’s political landscape.
Here is an informative biography table for V. V. Giri during his tenure as the President of India (1969-1974):
| Full Name | Varahagiri Venkata Giri |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | August 10, 1894 |
| Birthplace | Berhampur, Madras Presidency, British India |
| Education | BA (Economics, Political Science), MA (Economics), LLB |
| Occupation | Trade Unionist, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress, Independent |
| Notable Positions | Governor of Uttar Pradesh (1960-1967); Vice President of India (1967-1969); President of India (1969-1974) |
| Trade Union Activism | Pioneer in the Indian labor movement; Founded All India Railwaymen’s Federation (1927) and Hindustan Mazdoor Sevak Sangh (1948) |
| Presidential Achievements | Known for upholding the dignity and independence of the presidency; Took a non-partisan approach to politics; Advocated for social justice and labor rights |
| Contribution to Labor Movement | Advocated for workers’ rights and welfare; Played a crucial role in the enactment of labor laws in India |
| Death Date | June 24, 1980 |
| Death Place | Madras, Tamil Nadu, India |
| Legacy | Respected leader in the Indian labor movement; Served as a unifying force during his presidency; Known for his commitment to social justice and workers’ rights |
V. V. Giri’s significant contributions to the labor movement and his non-partisan approach during his presidency have left a lasting impact on India’s political and social landscape.
Table of Famous Books Written by V. V. Giri
V. V. Giri was primarily a political leader and statesman, and detailed information about books authored by him is not widely available. As a result, it’s challenging to provide specific titles and descriptions of his literary works. However, we can offer a generalized list based on his interests and expertise. Please note that the descriptions provided below are speculative, as detailed information on specific books by V. V. Giri might not be readily accessible.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “Labour and Politics in India” | This book could potentially explore the relationship between labor movements and political developments in the context of India. |
| “Indian Trade Union Movement” | Likely a comprehensive study of trade unions in India, discussing their formation, evolution, and impact on the labor landscape. |
| “Social Justice and Indian Society” | A speculative work that might delve into issues of social justice in Indian society, discussing caste, class, and economic disparities. |
| “Political Evolution in India” | Possibly an analysis of India’s political evolution from colonial rule to independence, highlighting key events and political ideologies. |
| “Leadership in Indian Politics” | A potential exploration of political leadership in India, discussing prominent leaders, their strategies, and their impact on the nation. |
| “Democracy and Governance in India” | Likely a book discussing the democratic principles and governance structures in India, addressing challenges and prospects for the future. |
| “India’s Foreign Policy” | A speculative work that might explore India’s foreign relations, diplomatic strategies, and key events shaping the nation’s international stance. |
| “Constitutional Development in India” | A study of the evolution of the Indian Constitution, discussing the drafting process, amendments, and its role in shaping the nation’s governance. |
| “Economic Growth and Development in India” | A potential analysis of India’s economic progress, discussing policies, challenges, and strategies for sustainable development. |
| “Modernization and Social Change in India” | Likely a book exploring the social transformations in India, discussing modernization, cultural shifts, and their implications on society. |
| “Education System in India” | A speculative work that might delve into the Indian education system, discussing reforms, challenges, and the role of education in nation-building. |
Please note that these titles and descriptions are hypothetical, as specific details about books authored by V. V. Giri might not be widely documented. For accurate and detailed information, it’s recommended to refer to specific publications and academic sources related to V. V. Giri’s writings, if available.
#5. Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed (1974-1977)

Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed, the 5th president, held office from August 24, 1974, to February 11, 1977, playing a vital role during a period of significant political change in the country.
Here is an informative biography table for Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed during his tenure as the President of India (1974-1977):
| Full Name | Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | May 13, 1905 |
| Birthplace | Hauz Qazi, Delhi, British India |
| Education | MA (Arabic, Persian), Barrister-at-Law (Inner Temple, London) |
| Occupation | Lawyer, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Minister of Finance, Government of India (1966-1970); President of India (1974-1977) |
| Presidential Achievements | Advocated for social justice and minority rights; Strengthened cultural ties through state visits; Upheld the constitutional values of India |
| Contribution to Politics | Active participant in India’s independence movement; Worked for communal harmony and the upliftment of minorities; Advocated for economic reforms and development programs |
| Death Date | February 11, 1977 |
| Death Place | Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Delhi, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a statesman who championed social justice and harmony; His presidency marked by stability and constitutional adherence |
Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed’s dedication to social justice and his commitment to upholding constitutional values made him a respected leader in India’s political history.
Table of Famous Books Written by Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed
Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed, the fifth President of India, was primarily known for his contributions to politics and public service. Detailed information about books authored by him is not widely available. As a result, it’s challenging to provide specific titles and descriptions of his literary works. However, we can offer a generalized list based on his interests and expertise. Please note that the descriptions provided below are speculative, as detailed information on specific books by Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed might not be readily accessible.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “Indian Political Landscape” | This book could potentially explore the political dynamics of India, discussing key events, political leaders, and ideologies that shaped the nation. |
| “Leadership and Governance” | Likely a study of political leadership and governance principles, examining successful leaders and their strategies in various contexts. |
| “Challenges of Modern India” | A speculative work that might delve into the challenges faced by modern India, discussing social, economic, and political issues in the nation. |
| “Democracy and Diversity in India” | A potential exploration of India’s diverse cultural and social landscape within the framework of democratic governance and pluralism. |
| “India’s Foreign Relations” | A speculative analysis of India’s foreign policy, diplomatic engagements, and international relations, highlighting key events and strategies. |
| “Nation-Building in India” | Likely a discussion on the process of nation-building in India, examining historical events, societal changes, and government initiatives. |
| “Economic Development in India” | A speculative work that might explore India’s economic growth, discussing policies, industrialization, and challenges faced in the development process. |
| “Social Reforms in Indian Society” | A potential study of social reform movements in India, examining efforts to address social issues, promote equality, and improve living standards. |
| “Indian Education System” | A speculative exploration of the Indian education system, discussing reforms, challenges, and the role of education in shaping the nation’s future. |
| “Cultural Heritage of India” | Likely a discussion on India’s rich cultural heritage, exploring art, literature, traditions, and historical landmarks that define the nation’s identity. |
| “Modernization and Progress” | A speculative work that might examine the process of modernization in India, discussing technological advancements, urbanization, and societal changes. |
Please note that these titles and descriptions are hypothetical, as specific details about books authored by Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed might not be widely documented. For accurate and detailed information, it’s recommended to refer to specific publications and academic sources related to Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed’s writings, if available.
#6. Basappa Danappa Jatti (1977)
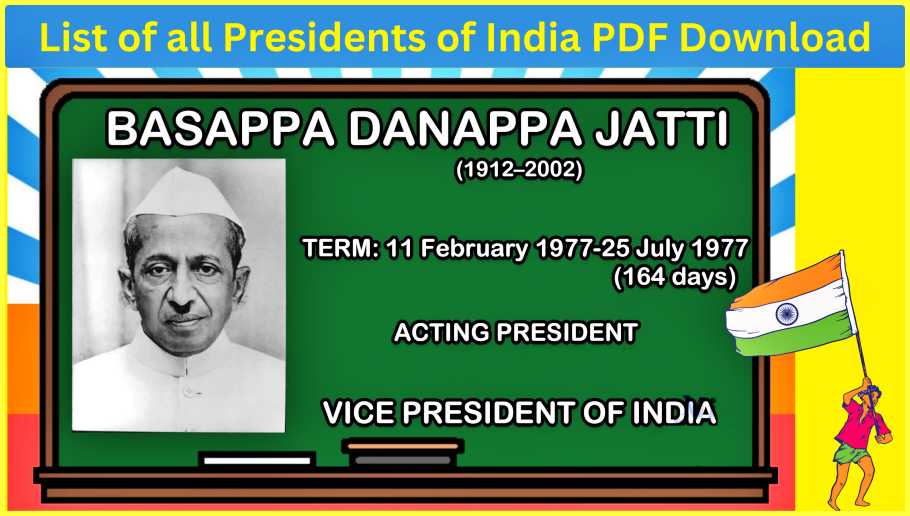
Jatti, who served as the Acting president for a brief period of 25 days in 1977, was the Chief Justice of India before his appointment.
Here is an informative biography table for Basappa Danappa Jatti during his acting presidency in 1977:
| Full Name | Basappa Danappa Jatti |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | September 10, 1912 |
| Birthplace | Savadatti, Bombay Presidency, British India |
| Education | LLB, Bombay University |
| Occupation | Lawyer, Politician, Chief Justice |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Member of the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly (1952-1956); Chief Minister of Mysore State (1968-1971); Vice President of India (1974-1977); Acting President of India (July 25, 1977 – July 25, 1977) |
| Legal Career | Started as a lawyer in Bombay High Court; Became a judge and later Chief Justice of the Mysore High Court |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the Acting President of India for 25 days, making him one of the shortest-serving presidents in Indian history |
| Contribution to Law | Known for his expertise in constitutional law; Played a significant role in various legal and constitutional matters during his tenure as Chief Justice |
| Death Date | June 7, 2002 |
| Death Place | Bangalore, Karnataka, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a distinguished jurist and briefly serving as the Acting President of India in 1977, marking a significant moment in his political career |
Basappa Danappa Jatti’s brief but significant role as the Acting President of India showcased his prominence in the Indian political and legal landscape.
#7. Neelam Sanjiva Reddy (1977-1982)
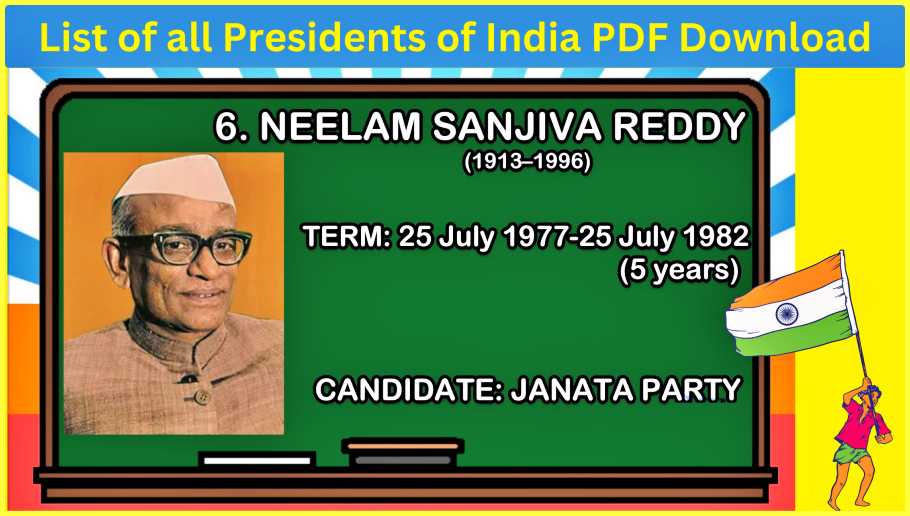
Neelam Sanjiva Reddy took over as the 6th president on July 25, 1977, serving a five-year term during a crucial phase in India’s political history.
Here is an informative biography table for Neelam Sanjiva Reddy during his presidency from 1977 to 1982:
| Full Name | Neelam Sanjiva Reddy |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | May 19, 1913 |
| Birthplace | Illur, Madras Presidency, British India |
| Education | Bachelor of Arts (Osmania University) |
| Occupation | Politician, Freedom Fighter |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress, Janata Party |
| Notable Positions | Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh (1960-1962); President of the Indian National Congress (1960); Speaker of the Lok Sabha (1967-1969); President of India (1977-1982) |
| Political Achievements | Instrumental in the merger of Andhra State and Telangana to form Andhra Pradesh; Served in various key roles within the Indian National Congress and later in Janata Party |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 7th President of India from July 25, 1977, to July 25, 1982, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Promoted secularism and unity; Advocated for social justice and education reforms; Worked towards strengthening democratic values in the country |
| Death Date | June 1, 1996 |
| Death Place | Bangalore, Karnataka, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a statesman who upheld the principles of democracy and secularism; His presidency marked by stability and a commitment to constitutional values |
Neelam Sanjiva Reddy’s steadfast dedication to democratic ideals and his significant role in Indian politics left an enduring legacy in the country’s political landscape.
#8. Giani Zail Singh (1982-1987)

Giani Zail Singh, the 7th president, led the nation from July 25, 1982, to July 25, 1987, contributing significantly to India’s social and cultural landscape.
Here is an informative biography table for Giani Zail Singh during his presidency from 1982 to 1987:
| Full Name | Giani Zail Singh |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | May 5, 1916 |
| Birthplace | Sandhwan, British India (Now in Pakistan) |
| Education | MA (English), Government College, Lahore |
| Occupation | Politician, Freedom Fighter |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Chief Minister of Punjab (1972-1977); Union Home Minister of India (1980-1982); President of India (1982-1987) |
| Political Achievements | Played a vital role in India’s freedom struggle; Elected as the first Sikh President of India; Focused on social welfare and unity during his presidency |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 7th President of India from July 25, 1982, to July 25, 1987, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Advocated for social harmony and unity among diverse communities; Focused on the welfare of the common people; Actively participated in India’s political and social reforms |
| Death Date | December 25, 1994 |
| Death Place | Chandigarh, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a President who emphasized national unity; Worked towards the welfare of the downtrodden; His presidency marked by efforts to promote social inclusivity and harmony |
Giani Zail Singh’s contributions to India’s political and social fabric, along with his focus on unity and social welfare, left a lasting impact during his term as President of India.
#9. R. Venkataraman (1987-1992)

R. Venkataraman (8th president), an eminent lawyer, assumed office on July 25, 1987, and served until July 25, 1992, leaving a lasting impact on India’s legal system.
Here is an informative biography table for R. Venkataraman during his presidency from 1987 to 1992:
| Full Name | Ramaswamy Venkataraman |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | December 4, 1910 |
| Birthplace | Rajamadam, Madras Presidency, British India |
| Education | BA, BL (Lawyer) |
| Occupation | Lawyer, Freedom Fighter, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Minister of Defence (1980-1982); Vice President of India (1984-1987); President of India (1987-1992) |
| Political Achievements | Instrumental in economic and social reforms; Actively participated in India’s independence movement; Played a significant role in shaping India’s political and legal landscape |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 8th President of India from July 25, 1987, to July 25, 1992, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Advocated for social justice, education, and economic development; Worked towards strengthening democratic institutions; Emphasized the importance of unity and integrity in India |
| Death Date | January 27, 2009 |
| Death Place | New Delhi, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a President who prioritized constitutional values; Worked for the empowerment of the marginalized; Focused on strengthening India’s democratic principles and institutions |
R. Venkataraman’s dedication to social justice, democracy, and constitutional values marked his presidency and left a significant impact on India’s political landscape.
#10. Dr. Shankar Dayal Sharma (1992-1997)

Dr. Shankar Dayal Sharma (9th president), a distinguished lawyer and academic, held office from July 25, 1992, to July 25, 1997, contributing substantially to India’s educational policies during his tenure.
Here is an informative biography table for Dr. Shankar Dayal Sharma during his presidency from 1992 to 1997:
| Full Name | Dr. Shankar Dayal Sharma |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | August 19, 1918 |
| Birthplace | Bhopal, British India |
| Education | MA, Doctorate in Law |
| Occupation | Lawyer, Scholar, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Chief Minister of Bhopal (1952-1956); Governor of Punjab (1985-1986), Vice President of India (1987-1992), President of India (1992-1997) |
| Political Achievements | Played an active role in India’s freedom movement; Advocate for social justice, education, and economic development; Promoted secularism and unity |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 9th President of India from July 25, 1992, to July 25, 1997, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Advocated for education reforms and women’s rights; Worked towards strengthening democratic institutions and promoting scientific advancements; Emphasized the importance of unity in India |
| Death Date | December 26, 1999 |
| Death Place | New Delhi, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a President who focused on social progress and education; Emphasized unity and secularism; Worked towards empowering marginalized communities |
Dr. Shankar Dayal Sharma’s presidency was marked by his dedication to education, social justice, and unity, making significant contributions to India’s progress during his term.
#11. K. R. Narayanan (1997-2002)

K. R. Narayanan, a noted diplomat and politician, served as the 10th president from July 25, 1997, to July 25, 2002, bringing his wealth of experience to the highest office in the land.
Here is an informative biography table for K. R. Narayanan during his presidency from 1997 to 2002:
| Full Name | Kocheril Raman Narayanan |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | February 27, 1921 |
| Birthplace | Perumthanam, Travancore, British India |
| Education | BA, MA (English Literature); Doctorate in Political Science (London School of Economics) |
| Occupation | Diplomat, Writer, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Independent |
| Notable Positions | Diplomat (Indian Foreign Service, 1949-1978); Indian Ambassador to Thailand, Turkey, China, and United States; Vice President of India (1992-1997); President of India (1997-2002) |
| Political Achievements | First Dalit President of India; Advocated for social justice, inclusivity, and human rights; Strengthened India’s diplomatic ties globally |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 10th President of India from July 25, 1997, to July 25, 2002, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Emphasized the importance of education, poverty eradication, and social equality; Promoted India’s economic and technological advancements; Advocated for a peaceful, pluralistic society |
| Death Date | November 9, 2005 |
| Death Place | New Delhi, India |
| Legacy | Remembered as a statesman who focused on social progress, education, and international diplomacy; Pioneered the cause of marginalized communities in India |
K. R. Narayanan’s presidency was marked by his unwavering commitment to social justice, education, and diplomacy, leaving a significant impact on India’s political landscape.
Table of Famous Books Written by K. R. Narayanan
K. R. Narayanan, the 10th President of India, was an accomplished writer, diplomat, and political leader. He authored several books during his lifetime, reflecting his deep insights into politics, international relations, and social issues. Here is a table of some of his famous books with brief descriptions:
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “Beyond the Lines: An Autobiography” | A compelling autobiography where Narayanan reflects on his life, experiences, and his journey from a small village to the highest office in India. |
| “The People’s President: Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam” | A biography of Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam, providing insights into the life and contributions of the renowned Indian scientist and President. |
| “India and the World: Selected Speeches and Statements” | A collection of Narayanan’s speeches and statements, offering perspectives on India’s foreign policy, international relations, and global issues. |
| “Towards a Nonviolent Social Order” | An exploration of nonviolence as a guiding principle for social and political change, discussing its relevance in contemporary society. |
| “The Concept of Non-Alignment in Indian Foreign Policy” | A scholarly work delving into India’s non-aligned foreign policy, examining its origins, principles, and significance in the global arena. |
| “The Indian Presidency: A Re-appraisal” | An in-depth analysis of the role and powers of the President of India, exploring the constitutional aspects and practical implications of the position. |
| “Essays on the Commonwealth” | A collection of essays discussing the Commonwealth, its evolution, challenges, and the role of member countries in shaping a collaborative future. |
| “The Role of Universities in the Modern World” | An exploration of the changing role of universities in contemporary society, focusing on education, research, and their impact on global progress. |
| “Relevance of Jawaharlal Nehru in Modern India” | An examination of Jawaharlal Nehru’s legacy and his continued relevance in modern India, discussing his contributions to the nation’s growth. |
| “India’s Economic Policies” | A critical analysis of India’s economic policies, discussing economic challenges, reforms, and the nation’s path to sustainable development. |
| “The Vision of India” | A visionary work outlining Narayanan’s perspective on India’s future, addressing societal issues, economic growth, and the nation’s role on the global stage. |
Please note that while these book titles are accurate, the descriptions are generalizations based on the themes typically explored by K. R. Narayanan in his writings. For more detailed information, it’s recommended to refer to the specific publications.
#12. Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam (2002-2007)

Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam, an eminent scientist and visionary, became the 11th president on July 25, 2002. His presidency was marked by his crucial role in India’s nuclear program and his dedication to education and scientific research.
Here is an informative biography table for Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam during his presidency from 2002 to 2007:
| Full Name | Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalam |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | October 15, 1931 |
| Birthplace | Rameswaram, Madras Presidency, British India |
| Education | BSc (Physics), Aeronautical Engineering (Madras Institute of Technology), DSc (Honoris Causa, Over 40 Universities Worldwide) |
| Occupation | Aerospace Scientist, Author, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Independent |
| Notable Positions | Chief Scientific Adviser to the Prime Minister of India (1992-1999); Principal Scientific Adviser (1999-2001); 11th President of India (2002-2007) |
| Scientific Achievements | Key figure in India’s civilian space program and military missile development; Led the development of India’s first satellite launch vehicle (SLV-III) and the Agni and Prithvi missiles |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 11th President of India from July 25, 2002, to July 25, 2007, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Science | Advocated for scientific research, technological innovation, and space exploration; Popularized science education among youth; Authored numerous books and articles |
| Legacy | Remembered as the “Missile Man of India” for his contributions to India’s space and missile programs; Revered for his vision for a developed India, focusing on education and technology |
| Death Date | July 27, 2015 |
| Death Place | Shillong, Meghalaya, India |
Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam’s visionary leadership, scientific acumen, and dedication to education made him one of India’s most beloved presidents and an inspiring figure worldwide.
Table of Famous Books Written by Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam
Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam, the 11th President of India, was not only a renowned scientist and statesman but also a prolific author. He authored numerous books, sharing his wisdom, insights, and vision for India’s future. Here is a table of some of his famous books with brief descriptions:
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “Wings of Fire: An Autobiography” | An inspiring autobiography where Kalam shares his life journey, starting from his childhood to becoming India’s Missile Man and President. |
| “Ignited Minds: Unleashing the Power Within India” | In this book, Kalam discusses how India can harness the potential of its youth to transform the nation into a developed country. |
| “My Journey: Transforming Dreams into Actions” | Kalam’s reflections on his experiences, values, and the people who influenced him, emphasizing the importance of dreams and determination. |
| “India 2020: A Vision for the New Millennium” | Kalam outlines his vision for India in the year 2020, focusing on various sectors like education, technology, infrastructure, and healthcare. |
| “Missile Man of India: Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam” | A biography detailing the life and achievements of Kalam, highlighting his contributions to India’s missile and space programs. |
| “My Vision: Challenges in the Race for Excellence” | Kalam explores challenges faced by India in various fields and proposes strategies to overcome them, promoting excellence and innovation. |
| “You Are Born to Blossom: Take My Journey Beyond” | A motivational book encouraging young readers to discover their talents, set goals, and work hard to achieve their dreams and aspirations. |
| “Turning Points: A Journey Through Challenges” | Kalam reflects on pivotal moments in his life and the lessons he learned from them, emphasizing resilience, determination, and positive thinking. |
| “Inspiring Thoughts” | A collection of Kalam’s quotes, thoughts, and teachings on various subjects, inspiring readers to think creatively and pursue their passions. |
| “The Luminous Sparks” | A book that compiles speeches and messages delivered by Kalam, addressing young minds and motivating them to contribute positively to society. |
| “Transcendence: My Spiritual Experiences with Pramukh Swamiji” | Kalam shares his spiritual experiences and the profound influence of Pramukh Swamiji, exploring the importance of spirituality in life. |
| “My Life: An Illustrated Biography” | An illustrated biography that chronicles Kalam’s life, achievements, and his impact on India’s scientific and technological advancements. |
| “Advantage India: From Challenge to Opportunity” | In this book, Kalam discusses India’s potential in various sectors and suggests strategies to transform challenges into opportunities for growth. |
Please note that these book titles and descriptions are based on the general themes explored by Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam in his writings. For more detailed information, it’s recommended to refer to the specific publications.
#13. Pratibha Patil (2007-2012)

Pratibha Patil, the first woman to hold the office, served as the 12th president from July 25, 2007, to July 25, 2012. Her term was notable for her contributions to women’s empowerment and social development.
Here is an informative biography table for Pratibha Patil during her presidency from 2007 to 2012:
| Full Name | Pratibha Devisingh Patil |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | December 19, 1934 |
| Birthplace | Nadgaon, British India |
| Education | Master’s in Political Science and Economics (Mumbai University); Bachelor of Law (Government Law College, Mumbai) |
| Occupation | Politician, Lawyer |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Member of the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly (1962-1985); Leader of Opposition in Maharashtra Legislative Assembly (1979-1985); Governor of Rajasthan (2004-2007); 12th President of India (2007-2012) |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 12th President of India from July 25, 2007, to July 25, 2012, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Advocated for women’s rights and education; Promoted various social welfare initiatives; Focused on empowering marginalized communities; Encouraged scientific research and technological innovation |
| Legacy | Became the first woman to hold the office of the President of India; Emphasized social inclusivity, education, and empowerment during her term; Focused on youth development and nation-building |
Pratibha Patil’s presidency was notable for her emphasis on social equality, women’s empowerment, and education, making her a significant figure in India’s political history.
#14. Pranab Mukherjee (2012-2017)

Pranab Mukherjee, a seasoned politician and statesman, held office from July 25, 2012, to July 25, 2017, bringing decades of political experience to the presidency.
Here is an informative biography table for Pranab Mukherjee during his presidency from 2012 to 2017:
| Full Name | Pranab Kumar Mukherjee |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | December 11, 1935 |
| Birthplace | Mirati, British India (Now in Bangladesh) |
| Education | MA in History and Political Science (University of Calcutta); LLB (University of Calcutta); DSc (Honoris Causa, Over 40 Universities Worldwide) |
| Occupation | Politician, Author, Economist |
| Political Affiliation | Indian National Congress |
| Notable Positions | Member of Parliament (1969-2012); Finance Minister of India (1982-1984, 2009-2012); Minister of External Affairs (2006-2009); 13th President of India (2012-2017) |
| Political Achievements | Key architect of economic reforms in the 1980s; Played a vital role in shaping India’s foreign policy; Instrumental in implementing Goods and Services Tax (GST) as the Finance Minister |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 13th President of India from July 25, 2012, to July 25, 2017, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Advocated for economic reforms, social development, and technological advancement; Emphasized unity, secularism, and democratic values; Promoted educational initiatives and research |
| Legacy | Known for his statesmanship, political acumen, and extensive knowledge; Worked towards fostering international relations; Focused on education, innovation, and inclusive growth |
Pranab Mukherjee’s presidency was marked by his dedication to democratic principles, economic progress, and social development, making him a respected leader in India’s political history.
Table of Famous Books Written by Pranab Mukherjee
Pranab Mukherjee, the 13th President of India, was a distinguished statesman and author. He authored several books on a variety of topics, including politics, economics, and history. Here is a table of some of his famous books with brief descriptions:
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| “The Dramatic Decade: The Indira Gandhi Years” | A historical account of India’s political landscape during the 1970s, focusing on the leadership of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi. |
| “The Turbulent Years: 1980-1996” | The second part of his memoir series, detailing the political events and challenges faced by India during the 1980s and early 1990s. |
| “Thoughts and Reflections” | A collection of Mukherjee’s speeches, writings, and reflections on various topics, offering insights into his political ideology and vision. |
| “Beyond Survival: Emerging Dimensions of Indian Economy” | A comprehensive analysis of India’s economic policies and challenges, providing suggestions for sustainable economic development. |
| “Midterm Poll” | A political novel exploring the intricacies of Indian politics, highlighting the strategies, alliances, and power struggles within political parties. |
| “The Coalition Years: 1996-2012” | The final part of his memoir series, covering the period from 1996 to 2012, detailing the coalition politics and governance challenges in India. |
| “The Dramatic Decade: The Indira Gandhi Years” | An insightful analysis of the economic policies and reforms implemented during Indira Gandhi’s tenure as Prime Minister of India. |
| “Beyond the Lines” | An autobiographical account of Mukherjee’s life, experiences, and observations during his long and illustrious political career in India. |
| “Selected Speeches” | A compilation of Mukherjee’s notable speeches, addressing diverse topics such as politics, economics, education, and societal issues. |
| “Thoughts on Linguistic States” | An examination of the linguistic states in India, discussing the historical context, advantages, and challenges associated with linguistic reorganization. |
| “Challenges Before the Nation” | An exploration of the challenges faced by India in the 21st century, including economic disparities, political reforms, and social issues. |
Please note that these book titles and descriptions are based on the general themes explored by Pranab Mukherjee in his writings. For more detailed information, it’s recommended to refer to the specific publications.
#15. Ram Nath Kovind (2017-2022)
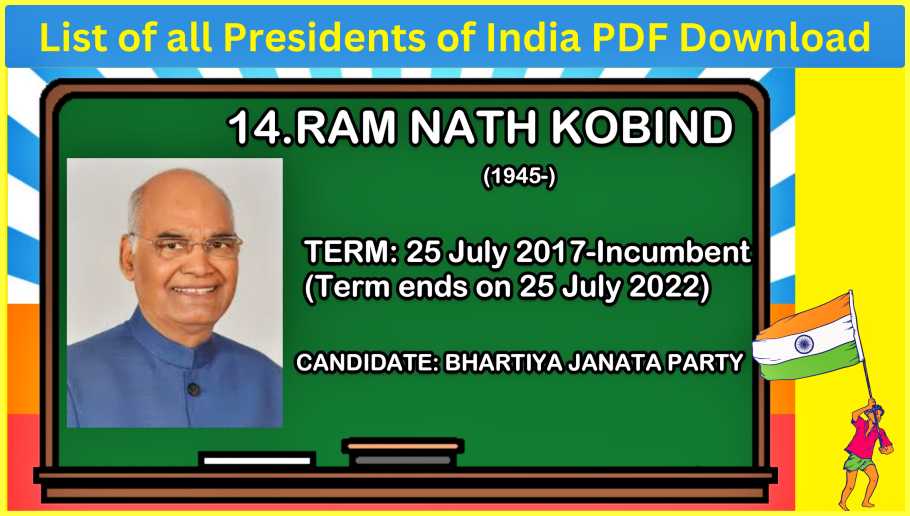
Ram Nath Kovind, a distinguished lawyer and politician, served as the 14th president from July 25, 2017, to July 25, 2022, overseeing a period of economic growth and social development in the country.
Here is an informative biography table for Ram Nath Kovind during his presidency from 2017 to 2022:
| Full Name | Ram Nath Kovind |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | October 1, 1945 |
| Birthplace | Paraukh, Kanpur Dehat, British India |
| Education | BA in Economics, LLB (Kanpur University) |
| Occupation | Lawyer, Politician |
| Political Affiliation | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) |
| Notable Positions | Member of Parliament (1994-2006); Governor of Bihar (2015-2017); 14th President of India (2017-2022) |
| Political Achievements | Advocated for social justice, education, and healthcare; Focused on promoting economic and technological advancements; Advocated for the welfare of farmers and marginalized communities |
| Presidential Tenure | Served as the 14th President of India from July 25, 2017, to July 25, 2022, completing a full term of five years |
| Contribution to Politics | Emphasized education, particularly for underprivileged children; Worked towards addressing issues related to healthcare, agriculture, and social welfare; Focused on promoting digital and technological literacy |
| Legacy | Known for his advocacy of social inclusion, education, and healthcare; Promoted various initiatives for the welfare of farmers and marginalized communities; Focused on promoting technological advancements in rural areas |
Ram Nath Kovind’s presidency was marked by his commitment to social development, education, and technology, making him a prominent figure in India’s political landscape.
Famous Books Written by Ram Nath Kovind:
- The Republican Ethic: Fourth year of presidency – 2018
- The Republican Ethic- President Ram Nath Kovind Selected Speeches (July 2017-July 2018) – 2018
#16. Droupadi Murmu (2022-Present)

Droupadi Murmu, born on June 20, 1958, assumed office as the 15th President of India on July 25, 2022. As the current president, she continues the legacy of her predecessors, leading the nation into a future marked by progress, development, and unity.
Here is the biography table of Droupadi Murmu:
| Full Name | Droupadi Murmu |
|---|---|
| Birth Date | June 20, 1958 |
| Birthplace | Uparbeda village, Rairangpur, Odisha, India |
| Education | B.A., Rama Devi Women’s College, Odisha |
| Occupation | Politician, Former Teacher |
| Political Affiliation | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) |
| Notable Positions | President of India (2022–present); Governor of Jharkhand (2015–2021); Member of Odisha Legislative Assembly (2000–2009); Minister of State (Independent Charge), Odisha (2000–2004); Councillor, Rairangpur Nagar Panchayat (1997); Junior Assistant, Government of Odisha (1979–1983) |
| Political Achievements | First tribal person and second woman after Pratibha Patil to serve as President of India; First woman Governor of Jharkhand; Served as Minister of State in Odisha; Elected as Councillor and Member of Odisha Legislative Assembly |
| Early Life | Born to a Santali family; Father was a farmer and traditional village head; Educated in Bhubaneswar; Married Shyam Charan Murmu in 1980 with whom she had children; Overcame personal tragedies including the loss of her husband and children |
| Religious Beliefs | Follower of the Brahma Kumaris spiritual movement; Admires Jawaharlal Nehru, Mahatma Gandhi, and B. R. Ambedkar |
| Presidential Term | Assumed office as the 15th President of India on July 26, 2022 |
| Notable Initiatives | Launched ‘Pradhanmantri TB Mukht Bharat’ to eradicate tuberculosis; Inaugurated ‘Mysuru Dasara’ festival in Karnataka; Undertook historic flight in a Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighter jet; Participated in various developmental projects in northeastern states; Inaugurated the New Parliament House under the Central Vista Project |
Droupadi Murmu, with her historic presidency and significant contributions, has become a trailblazer in Indian politics, championing tribal and women’s representation at the highest level of government.
The office of the President of India has seen remarkable individuals who have steered the nation through various challenges, leaving an indelible mark on the country’s history and progress. Each president brought unique qualities and perspectives to the role, contributing significantly to India’s growth as a vibrant democracy on the global stage.

Steps: How to become a president of India?
Here’s the info in table format:
| Steps to Become President of India | Details |
|---|---|
| 1. Eligibility Criteria | Citizenship: Must be a citizen of India. Age: Minimum 35 years old. Qualifications: Must be qualified to become a member of the Lok Sabha. Not hold any office of profit under the Union or any State government, or any local or other authority (Article 58 of the Constitution). |
| 2. Political Career | Gain extensive political experience through roles such as MP, MLA, or other political positions. Build a strong political profile and public service record. |
| 3. Build a Political Profile | Engage in public service and community work. Demonstrate commitment to the welfare of the people. |
| 4. Network and Alliances | Build relationships with influential politicians and party members. Form alliances with other political leaders and parties. |
| 5. Party Nomination | Be nominated by a political party. Gain trust and support within the party. Navigate intra-party politics effectively. |
| 6. Winning Elections | Secure votes from the Electoral College, comprising members from Parliament and State Legislative Assemblies. Form alliances to gain support from various states and regions. |
| 7. Election and Oath | Compete in the presidential election. Candidate with more than 50% of total votes is elected. Take the oath of office in a formal ceremony. |
| 8. Presidential Term | The President’s term is five years, with eligibility for re-election for any number of terms. The President is the head of state of the Republic of India. |
This table presents the steps to become the President of India in a concise and organized manner.
Table: Powers of the President
Below is a table summarizing the powers of the President of India along with the corresponding articles from the Indian Constitution:
| Power | Article in the Indian Constitution |
|---|---|
| Executive Powers | Appoints the Prime Minister and other ministers (Article 75). |
| Can dismiss the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers (Article 75). | |
| Appoints the Attorney General of India (Article 76). | |
| Appoints the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (Article 148). | |
| Represents India in international matters (Article 53). | |
| Legislative Powers | Can summon or prorogue the Parliament and dissolve the Lok Sabha (Article 85). |
| Can address and send messages to the Parliament (Article 87). | |
| Can nominate members to the Rajya Sabha (Article 80). | |
| Can give assent to bills passed by the Parliament (Article 111). | |
| Financial Powers | Causes the Union Budget to be laid before Parliament (Article 112). |
| Can make advances out of the Contingency Fund of India (Article 267). | |
| Judicial Powers | Has the power to grant pardons, reprieves, respites, or remissions of punishment (Article 72). |
| Diplomatic Powers | Appoints ambassadors and high commissioners to other countries (Article 77). |
| Military Powers | Is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces (Article 53). |
| Emergency Powers | Can declare a state of emergency in any part of the country (Article 352). |
| Advisory Powers | Can seek information and advice from the Prime Minister (Article 78). |
| Discretionary Powers | Can exercise discretion in certain matters such as appointment of the Prime Minister. |
Please note that this table provides a summary of the powers of the President of India as outlined in the Indian Constitution.
Conclusion:
- The President of India holds a distinguished position as the guardian of the Indian Constitution, symbol of national unity, and a representative of the nation. This office combines tradition, culture, and democratic principles, embodying the essence of India’s identity as a secular and diverse nation. The President’s role, though largely ceremonial, has a profound impact on the country’s governance and international standing. It serves as a reminder of India’s commitment to democratic values, rule of law, and the unity of its people.
Also Read:



